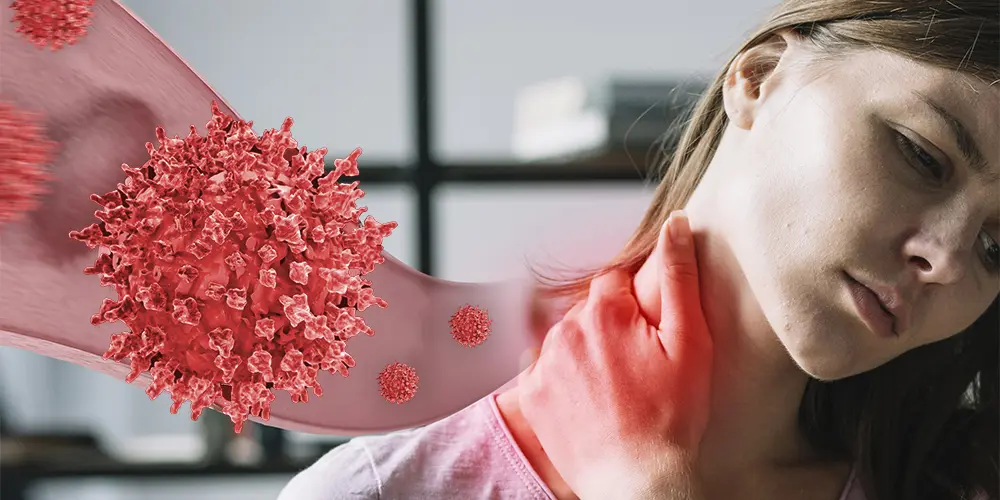
You must have the basic knowledge about allergy. If you’ve ever had sneezing, itchy eyes, or a runny nose during allergy season, you’re not alone. These are common signs of an allergic reaction to things like pollen, dust, or pet hair. But sometimes, you also notice something different—swollen glands, especially in the neck. So, the big question is, can allergies cause glands to swell?
Let’s break it down in a simple and friendly way so you can understand why your glands might feel swollen, what’s really going on inside your body, and when you should see a doctor.
What are swollen glands?
Swollen glands means a tiny, bean-shaped part of your body’s immune system. When individuals say “swollen glands,” they generally mean swollen lymph nodes. You can have swollen glands all over your body, such as in your chest, groin, armpits, neck, and other areas.
Lymph nodes are like filters. They help your body fight off germs, remove waste, and trap harmful things like bacteria and viruses. When they swell, it usually means your body is trying to protect itself from something.
Can allergies make your glands swell?
In most cases, regular allergies like pollen, dust, or animal dander don’t directly cause swollen lymph nodes. But that doesn’t mean there’s no connection.
Here’s what can happen:
- Allergies can cause stuffy sinuses and a lot of mucus.
- That drainage from your sinuses can lead to irritation or infection.
- If an infection develops (like a sinus infection), your lymph nodes may swell in response.
So, while allergies may not be the main reason, they can start a chain reaction that leads to swelling.
When can allergies lead to serious swelling?
Some types of allergies are more serious. For example, allergies to:
- Certain foods (like peanuts or shellfish)
- Medicines (such as antibiotics)
- Insect bites or stings
These can cause stronger body reactions. Swelling from these allergies might happen not only in your lymph nodes but also in other parts of the body—like your lips, face, or throat. This can be dangerous and may lead to a serious condition called anaphylaxis, which needs fast medical help.
What do swollen glands feel like?
When you have lymph nodes, you feel small lumps under your skin. They might:
- Be tender or sore
- Feel bigger than usual
- Move slightly when you touch them
- Be found in your neck, under your jaw, or behind your ears
Sometimes, you may also feel tired or have other symptoms depending on the cause.
What the lymphatic system does
To understand swelling better, it helps to know how your lymphatic system works.
This system is a main part of your immune defense. It comprises lymph fluids, lymph nodes, lymph fluid, and vessels that travel this fluid around your body. It helps.
- Remove waste and toxins
- Keep fluid levels balanced
- Fight infections and diseases
When your body senses a problem—like an infection or harmful invader—it sends white blood cells to help. These white blood cells collect in the lymph nodes, causing them to grow and swell.
Where are swollen glands usually noticed?
You have many lymph nodes, but some areas are more common for swelling, like
- Neck
- Jawline
- Armpits
- Groin area
Note: Usually, the glands near the part of the body that’s affected will swell. For example, the nodes in your neck may swell if you have a sore throat.
Common Reasons for swollen glands (Besides allergies)
While allergies don’t usually make glands swell on their own, here are some common causes that can:
1. Colds and flu
Common flu or cold-causing viruses may cause swollen glands. If you have, you may have:
- Cough
- Fever
- Body aches
- Sore throat
Note: This is a normal immune response and usually goes away in a week or two.
2. Sinus infections
If your allergies cause blocked sinuses, they might lead to a sinus infection. This can result in swollen glands around your face and neck, along with facial pressure, headache, and nasal congestion.
3. Strep throat and tonsillitis
Bacterial infections like strep throat can make the glands in your neck or under your jaw swell. This often comes with
- Severe sore throat
- Trouble swallowing
- White patches in the throat
- Fever
You may need antibiotics to treat it.
4. Ear infections
Infections in the ear can also lead to swelling in adjacent lymph nodes, especially around your neck and jaw.
5. Tooth and gum problems
Poor dental hygiene or gum infections can lead to swollen glands in your face or neck. An abscessed tooth (a pocket of pus caused by infection) is another possible reason.
6. Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
Certain STIs, such as gonorrhea or syphilis, can lead to swollen lymph nodes in your groin.
7. Autoimmune diseases
Conditions like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis can confuse your immune system into attacking healthy tissue. This condition may cause swollen glands and inflammation.
8. Cancer
In some rare cases, swollen lymph nodes can be a sign of cancer like lymphoma or leukemia. If the swelling lasts more than a few weeks or keeps getting worse, it’s important to see a healthcare provider.
9. Stress
Long-term stress can lower your immune system’s strength. While stress doesn’t directly lead to swollen glands, it can make you more likely to get infections, which is a source of swelling.
10. Certain medications
Certain drugs may lead your lymph nodes to swell. Generally, these medications are those used to treat malaria or control seizures. Always talk to your doctor if you notice swelling after starting a new medication.
How long do swollen glands last?
Usually, swollen lymph nodes go away in a week or two once your body fights off the infection. But if they stay swollen for longer, keep getting bigger, or are painful, it’s best to get checked out.
When to see a healthcare provider
It’s time to get medical help if you experience:
- The swelling lasts more than two weeks
- You also have a fever, night sweats, or weight loss
- The gland keeps getting larger
- You have trouble breathing or swallowing
- The lump feels very hard or doesn’t move when you touch it
Getting checked early can help rule out serious conditions and bring peace of mind.
Key takeaways
- Swollen glands usually mean your body is fighting something.
- Allergies alone don’t often cause lymph node swelling—but they can lead to issues that do.
- Many other conditions, like infections or autoimmune diseases, can also cause swollen glands.
- If the swelling doesn’t go away or comes with other symptoms, talk to your doctor.
Stay healthy, pay attention to your body, and don’t ignore unusual swelling—especially if you’re unsure what’s causing it. Whether it’s allergies or something more serious, getting help early can make all the difference.
Can allergies cause glands to swell? Final thoughts
In simple words—allergies usually don’t cause swollen glands by themselves, but they can lead to problems like sinus infections that might cause swelling. Serious allergic reactions (like to food or insect stings) can cause swelling in other parts of the body and should be treated right away.
If you’re not sure why your glands are swollen or if they’re not going away, don’t waste time and immediately set an appointment with your healthcare provider. It’s always better to be safe and find out what’s really going on.