More than 50% of the U.S. adult population faces gum disease, which is a health condition that ranges from mild to severe. Gingivitis is the early form of gum disease and can be managed with regular oral care, while periodontitis is the advanced stage, which, if left untreated, can cause tooth loss. But what sets these two conditions apart, and how can you differentiate them?
In this guide, we will explain you the differences between gingivitis and periodontitis, their signs and symptoms, treatments, and preventive measures that can assist you in maintaining healthy gums and a shiny smile.
Gingivitis vs. Periodontitis: Key Differences
Gingivitis and periodontitis are stages within the extensive category of gum disease, which is medically called periodontal disease. However, both conditions affect your gums, and they vary in their severity, progression, and treatment requirements. Here’s what you need to know so keep reading and stay connected with us to keep your gum teeth healthy.
Breaking Down the Terms: Gingivitis and Periodontitis
To differentiate these both gum conditions it is also important for you to understand their names first:
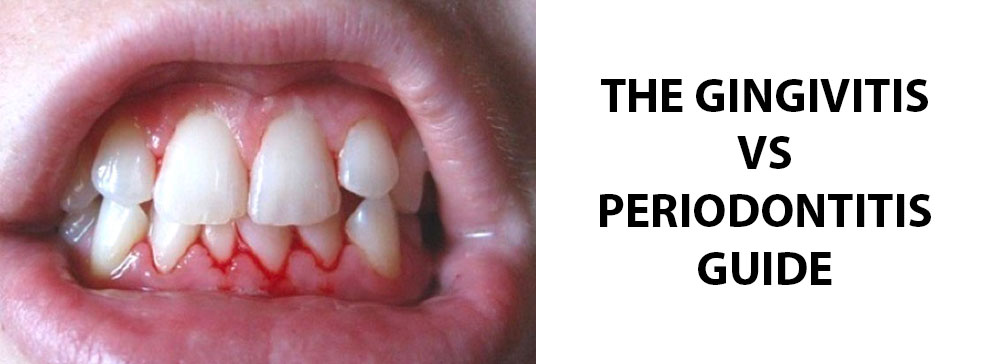
- Gingivitis: This term derives from “gingiv-“, which means the gums. It shows inflammation in your gum tissues and indicates the earliest, mildest form of gum disease.
- Periodontitis: “perio-” means “around” and “-don-” means “tooth,” this term refers to a condition that impacts both your gums and the supporting structures around the teeth, including connective tissues and the bone. Periodontitis occurs after gingivitis has advanced and causes severe symptoms, such as bone loss and gum recession.
Symptoms of Gingivitis
Gingivitis symptoms often start slowly but it can worsen if you don’t follow consistent dental care. Key indicators include:
- Red or darkened gum tissue
- Bad breath (halitosis)
- Sensitivity to temperature changes
- Swollen or puffy gums
- Bleeding during brushing or flossing
These symptoms indicate inflammation that, if you leave it untreated, can progress into periodontitis.
Symptoms of Periodontitis
Periodontitis, as we explained earlier, has more advanced signs, as it affects not only gums but also the structures supporting your teeth:
- Persistent bad breath
- Pain while chewing
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Deep pockets develop between your teeth and gums
- Gaps developing between teeth
- Due to advanced gum recession, that can lead to expose your roots of tooth
- Bone loss visible on dental X-rays
Periodontitis can be painful and eventually may cause tooth loss if not treated, emphasizing the importance of early recognition and treatment.
Causes and Risk Factors for Gum Disease
Both gingivitis and periodontitis shoot from plaque. However, plaque is a thin sticky layer of bacteria that multiplies on your gums and teeth. If you don’t remove this plaque, it hardens into tartar, which inflames your gums and causes gingivitis. If you don’t get proper treatment, gingivitis can transform into periodontitis as bacteria spread to nearby tissue.
Here we are providing you the list of factors that elevate the risk of developing your gum disease such as:
- Smoking or tobacco use
- Stress, which weakens immune function
- Hormonal changes (e.g., menopause, pregnancy)
- Poor oral hygiene habits
- Certain severe health conditions including heart disease and diabetes
- A diet high in sugars or lacking in essential nutrients
Identifying and addressing these risk factors can help prevent or minimize the severity of your gum disease.
How Gingivitis Progresses to Periodontitis
In most cases, untreated gingivitis can eventually progress into periodontitis. But this advancement doesn’t occur overnight. It depends on factors such as oral hygiene and immune health. It can take weeks to years for gingivitis to convert into full-blown periodontitis.
When gingivitis develops, plaque buildup leads to the gums to become inflamed. Over time, this inflammation expands below the gum line, where it affects the bone and connective tissues around your teeth, causing periodontitis.
Treatment Options for Gingivitis and Periodontitis
Treatment of gum disease typically depends on the stage of your gum condition. Luckily, both gingivitis and periodontitis are treatable with professional dental care and lifestyle changes.
Gingivitis Treatment
Gingivitis can often be reversed through:
- Regular Dental Cleanings: specialized dental cleanings can remove your plaque and tartar buildup that can’t be eradicated through brushing alone.
- Improved Oral Hygiene: Brushing at least two times a day and flossing daily are crucial for eliminating plaque from your teeth and gums.
- Antiseptic Mouthwash: Mouthwash can help decrease inflammation and bacteria, maintaining healthy gums.
Periodontitis Treatment
Since periodontitis is more rigorous, it needs more inclusive care:
- Medications: In some cases, antibiotics or antiseptic rinses may be prescribed to help manage infection and inflammation.
- Scaling and Root Planing: This deep-cleaning procedure eliminates tarter and plaque beneath your gum line. Your dentist will smooth the roots to prevent bacteria from reattaching.
- Laser Therapy: Laser treatment can target the infected tissue, to reduce your discomfort and promote your healing faster.
- Surgical Treatments: In advanced cases, gum or bone grafts may be necessary to restore lost tissue and support your teeth.
Natural Remedies and At-Home Care for Gum Disease
While professional care is significant for treating your gum disease, numerous home remedies may support healthy gums and ease early symptoms:
- Green Tea: Green tea is known for its anti-inflammatory properties; green tea may support your gum health when drunk regularly.
- Coconut Oil Pulling: Swishing with oil such as coconut oil may help you eliminate bacteria and reduce inflammation.
- Saltwater Rinse: Rinsing with salt water can ease swollen gums and support healing.
How TO Prevent Gum Disease
Prevention is the most useful approach to maintaining healthy gums. Here are some evidence-based ways by following you can prevent gum disease:
- Brush Twice a Day: With a soft-bristled brush.
- Floss Daily: Flossing can remove plaque between teeth where brushing may be neglected.
- Avoid Smoking: Tobacco use is a major risk factor for gum disease, making cessation a top priority.
- Consume a Balanced Diet: Nutrient-dense foods support your gum health and overall oral health.
- Visit Your Dentist Regularly: Biannual cleanings and examinations help prevent plaque buildup and recognize early signs of your gum disease.
When to Seek Professional Dental Help
If you experience persistent symptoms of gum disease, like receding gums, bleeding, or loose teeth, it’s crucial to visit your dentist. They can help the severity of your gum disease and suggest the best treatment options. Even if you are not noticing symptoms, regular dental checkups are key to early diagnosis and prevention.
Conclusion
Both gingivitis and periodontitis are forms of gum disease that impact millions of individuals worldwide. Understanding the difference between gingivitis and periodontitis can assist you in taking early action to protect your gums, prevent tooth loss, and maintain a healthy shiny smile. By combining good oral hygiene with regular dental visits, you can minimize your risk of gum disease and keep your mouth healthy for years.
FAQs
How is gingivitis different from periodontitis?
Gingivitis is the early stage of your gum disease, leading to bleeding and inflammation in the gums. Periodontitis is a progressed stage, in which you experience deep pockets, gum recession, and even tooth loss.
Is gingivitis reversible?
Yes, gingivitis is reversible, if you practice good oral hygiene and regular dental cleanings. Periodontitis, however, needs more thorough treatment.
Can gingivitis turn into periodontitis?
Yes, if you leave it untreated, gingivitis can turn into periodontitis, which may lead to more severe symptoms and potential bone loss.
What’s the main cause of gum disease?
Poor oral hygiene can lead to plaque and tartar buildup, which is the main cause of gum disease.
Can periodontitis be cured?
While it can’t always be completely cured, periodontitis can be managed with specialized treatment and better oral care.
What are the warning signs of periodontitis?
Warning signs of periodontitis are gum pain while chewing, recession, loose teeth, and bad breath.