Have you ever noticed puffiness or swelling under your skin that doesn’t seem to go away quickly? That soft, swollen area might be something called subcutis edema. It sounds like a big medical term, but don’t worry —we’re here to break it down in simple words.
In this blog, you’ll learn what subcutis edema is, what causes it, how to recognize the signs, and what you can do about it, both naturally and with medical help.
What is subcutis edema?
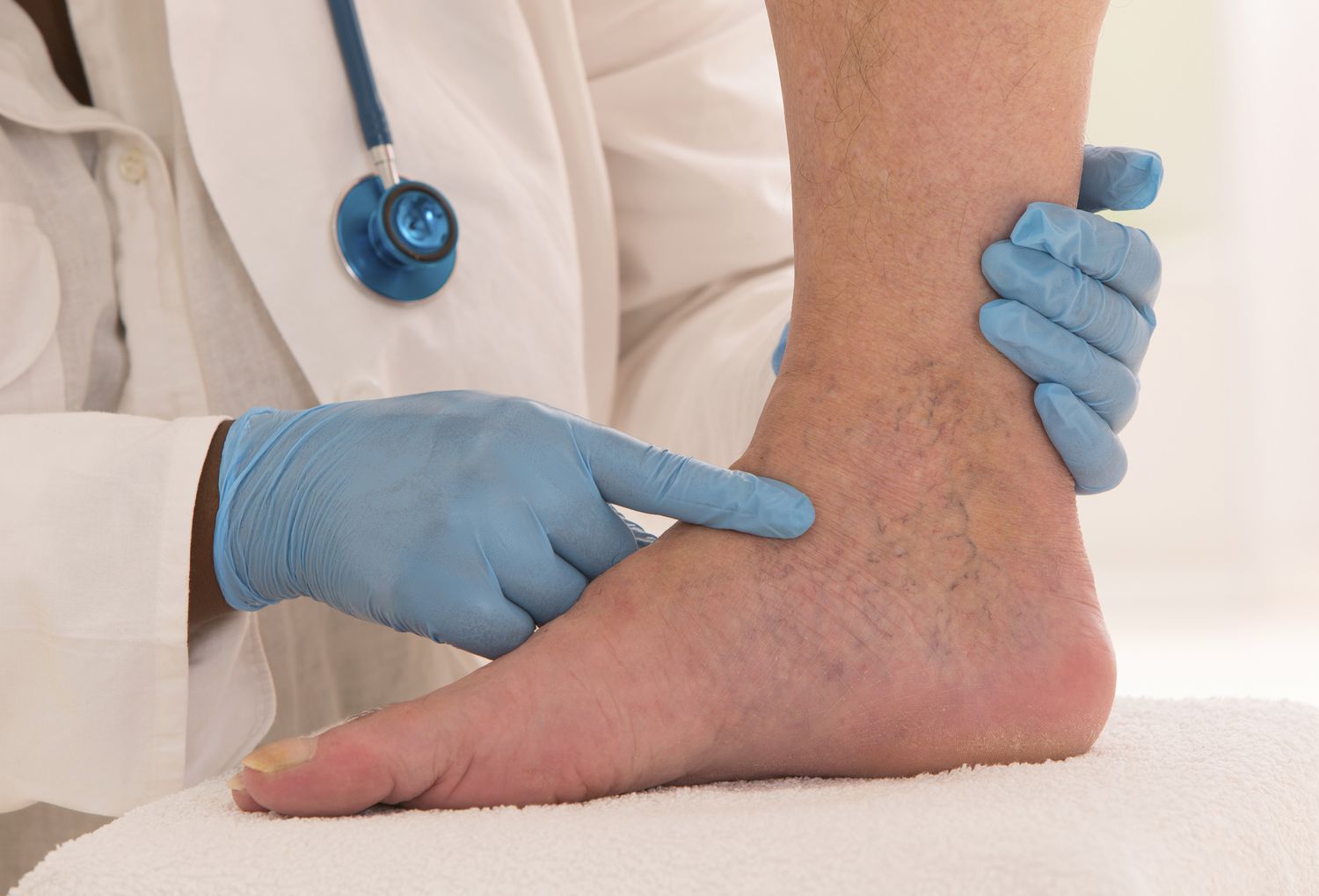
Subcutis edema (also known as subcutaneous edema) is a type of swelling that happens just under the skin. The word “subcutis” refers to the fat and tissue layer beneath your skin, and “edema” means swelling caused by fluid build-up.
So, when we say “subcutis edema,” we mean fluid has built up under the skin, causing it to look and feel swollen or puffy.
This condition is not a disease on its own. Instead, it’s often a sign of another health issue, like poor circulation, kidney problems, or even a reaction to medication.
Common causes of subcutaneous edema
There are several reasons why fluid may collect under your skin. Let’s explore and discuss the most common ones:
1. Poor Circulation
When blood does not flow well in your arms or legs, fluid can begin to build up in the tissues. This happens a lot in people with heart problems or those who sit or stand for long periods.
2. Kidney problems
Your kidneys help control the balance of water and salt in your body. If they aren’t working properly, too much fluid stays in your body, causing swelling.
3. Liver disease
A sick liver can affect how your body makes proteins that control fluid levels. If the balance is off, fluid can leak into the tissue under your skin.
4. Heart failure
If your heart can’t pump blood properly, fluid can start to collect in your legs, feet, or other parts of your body, including under the skin.
5. Infections and inflammation
Infections or allergic reactions can lead to swelling in your local area of body. If the inflammation is in the skin or nearby tissue, subcutis edema may develop.
6. Certain medicines
Some medications can lead your body to keep hold of to water. These may include steroids, high blood pressure drugs, and hormone treatments.
7. Pregnancy
Pregnancy changes your body in many ways. It can increase pressure on your veins, leading to water build-up under the skin — especially in the legs and feet.
Signs and Symptoms of Subcutaneous Edema
Subcutis edema often shows up as swelling or puffiness, but there are other signs too. Watch out for:
- Swelling that gets worse during the day
- Skin that feels tight, shiny, or warm
- A dent left on your skin when you press it with your finger (this is called “pitting”)
- Heavy or achy legs
- Difficulty moving joints if swelling is near them
Note: Swelling can occur on part of your body, but it most commonly happens in your face, legs, hands, feet, and ankles.
How is subcutis edema diagnosed?
If you think you have subcutis edema, it’s a good idea to see a doctor. They may ask:
- When did the swelling start?
- Does it get better when you lie down or rest?
- Are you taking any new medications?
Your healthcare provider may order you to do some tests, such as:
- Blood tests to check kidney, liver, or heart health
- Urine tests to see if your body is losing protein
- Ultrasound to check for blood clots or poor blood flow
- X-rays or CT scans in some cases
Note: Getting the right diagnosis is important so you can treat the root cause of the swelling.
Natural ways to help manage subcutis edema
In several mild cases, lifestyle changes may help ease and minimize swelling. Here are a few easy and natural ways to manage subcutis edema:
1. Elevate the swollen area
Raising the swollen area above the level of your heart helps fluid move back toward your heart. Try putting your legs up on pillows when lying down.
2. Move more
Sitting or standing too long can make swelling worse. Light exercise like walking or stretching helps improve blood flow and reduces fluid buildup.
3. Eat a low-salt diet
Your body can keep extra water if you consume extra salt in food. Cutting back on salty snacks and processed foods may help control swelling.
4. Drink more water
It may sound strange, but drinking more water can actually help your body get rid of extra fluid. Aim for 6 to 8 glasses a day, unless your doctor tells you otherwise.
5. Massage
If you gently massage the swollen area in the direction of your heart, this technique can help move the fluid out of the tissues. Be gentle, especially if your skin feels tight or sore.
6. Wear compression garments
Compression socks or sleeves can help push the fluid back into your bloodstream. These are helpful if you have swelling in your legs or arms.
7. Herbal remedies
Certain common and easily used herbs, such as ginger, dandelion, or parsley, are known to help minimize water retention. Always talk to a healthcare provider before trying herbs, especially if you’re on medication.
Medical treatments for subcutis edema
If natural methods don’t work or if your edema is caused by an underlying health issue, your doctor might recommend:
- Water pills (diuretics): These help your body get rid of extra fluid.
- Treatment for the underlying condition: Managing heart, liver, or kidney disease often helps reduce edema.
- Changing medications: If a drug you’re taking is causing swelling, your doctor may adjust your dose or switch it.
- Drainage or wound care: If there’s a lot of fluid buildup, special care may be needed to prevent infection.Sometimes, subcutis edema can be a sign of something serious. Call a doctor if you have:
- Redness, pain, and warmth in the swollen area
- Swelling that comes on suddenly
- Trouble breathing or chest pain
- Skin sores or infections near the swelling
- Swelling that doesn’t go away with rest
Subcutis edema and water retention: What’s the Link?
Subcutis edema is a form of water retention. Water retention happens when your body holds too much fluid. This can lead to bloating, puffiness, and a feeling of heaviness.
People with hormone problems, like PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome), are more likely to get water retention, especially in the legs, belly, and face.
Here are common signs of water retention you might see along with subcutis edema:
- Swollen hands or feet
- Rings or shoes feeling tight
- Puffy eyelids in the morning
- Weight that goes up and down quickly
- Stiff joints
- Tired or heavy feeling in the limbs
Note: If you have these symptoms often, your body may be holding too much water, and you should ask your doctor why it’s happening.
Conclusion
Subcutaneous edema might seem scary at first, but in many cases, it’s manageable — especially when you know what causes it and how to treat it.
The key is to listen to your body, stay active, eat a balanced diet, and get regular checkups. Whether it’s caused by something simple like standing too long or something more serious like a heart or kidney issue, don’t ignore the signs. The sooner you understand the cause, the sooner you can feel better.
Remember, you’re not alone. Many people experience this kind of swelling. With the right steps, you can reduce the puffiness and get back to feeling more like yourself.